
Introduction To MBBS IN Australian Medical Registration
In Australia, medical practitioners are required to be registered with the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA) in order to practice medicine legally. AHPRA is responsible for ensuring that the medical profession maintains high standards of competence and ethical behavior, and that patients receive safe and effective care.
To be eligible for medical registration in Australia, a person must have completed a medical degree or equivalent qualification from a recognized institution, and must have completed a period of supervised practice known as an internship. After completing their internship, doctors may apply for general registration, which allows them to practice medicine independently in Australia.
In addition to general registration, there are a number of specialist medical registers maintained by AHPRA. These registers cover a range of specialties including anesthetics, obstetrics and gynecology, psychiatry, and surgery. In order to be registered as a specialist, doctors must have completed advanced training in their chosen field, and must have demonstrated a high level of expertise and competence.
Quick Contact
AHPRA also sets the standards for continuing professional development (CPD) for medical practitioners in Australia. Doctors are required to undertake a certain amount of CPD each year in order to maintain their registration. This may include attending conferences and seminars, completing online courses, or engaging in other forms of professional development.
One of the key roles of AHPRA is to investigate complaints and concerns about the conduct or competence of medical practitioners. Members of the public can make a complaint to AHPRA if they have concerns about the care they have received from a doctor. AHPRA will investigate the complaint and may take disciplinary action if necessary, including suspending or cancelling a doctor’s registration.
In addition to AHPRA, the Medical Board of Australia (MBA) plays an important role in the regulation of the medical profession. The MBA is responsible for setting the standards for medical practice in Australia, and for developing and implementing policies and guidelines to support these standards.
The MBA is made up of a number of committees, including the Registration and Accreditation Committee, the Professional Performance Committee, and the Health Practitioner Tribunal. These committees are responsible for ensuring that medical practitioners in Australia adhere to the highest standards of professionalism and ethical conduct.
Overall, medical registration in Australia is a rigorous and highly regulated process designed to ensure that patients receive safe and effective care. By setting high standards for competence and ethical behavior, and by investigating complaints and concerns about medical practitioners, AHPRA and the MBA play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the medical profession in Australia.
| Authority | Description |
|---|---|
| Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA) | The AHPRA is the central organization responsible for regulating health practitioners in Australia. It partners with the 15 national boards to ensure that all medical practitioners meet the registration requirements before practicing in Australia. |
| 15 National Boards | There are 15 national boards in Australia, each responsible for the registration of a specific group of health practitioners. The Medical Board of Australia registers medical practitioners, while the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia registers nurses and midwives. IMGs must register with the Medical Board of Australia before practicing medicine in Australia. |
| Medical Board of Australia | The Medical Board of Australia sets standards for medical education and training and is responsible for ensuring that all medical practitioners, including IMGs, meet the registration requirements before practicing in Australia. It conducts assessments and issues certificates of registration. |
| States and Territory Boards & Committees | Each state and territory in Australia has its own board or committee responsible for the registration of medical practitioners. These boards and committees work under the guidance of the Medical Board of Australia to ensure that all medical practitioners meet the registration requirements. |
| Australian Medical Council (AMC) | The AMC sets standards for medical education and training in Australia and assesses the qualifications of IMGs to ensure that they meet the required standards for practicing medicine in Australia. |
IMGs need to pass the AMC’s exams to be eligible for registration with the Medical Board of Australia. The AMC exams assess the IMGs’ knowledge and clinical skills to ensure that they are safe to practice medicine in Australia.
Becoming a doctor in Australia requires a thorough understanding of the various authorities responsible for medical registration. The Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA), 15 National Boards, Medical Board of Australia, States and Territory Boards & Committees, and Australian Medical Council all play a crucial role in the registration process.
IMGs must register with the Medical Board of Australia and pass the Australian Medical Council’s exams to be eligible to practice medicine in Australia. It is important for IMGs to familiarize themselves with the requirements and standards set by these authorities to ensure a smooth registration process.
Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA)
15 National Boards
Medical Board of Australia
States and Territory Boards and Committees
Australian Medical Council
National Registration and Accreditation Scheme (NRAS)
Types of Australian Medical Registration
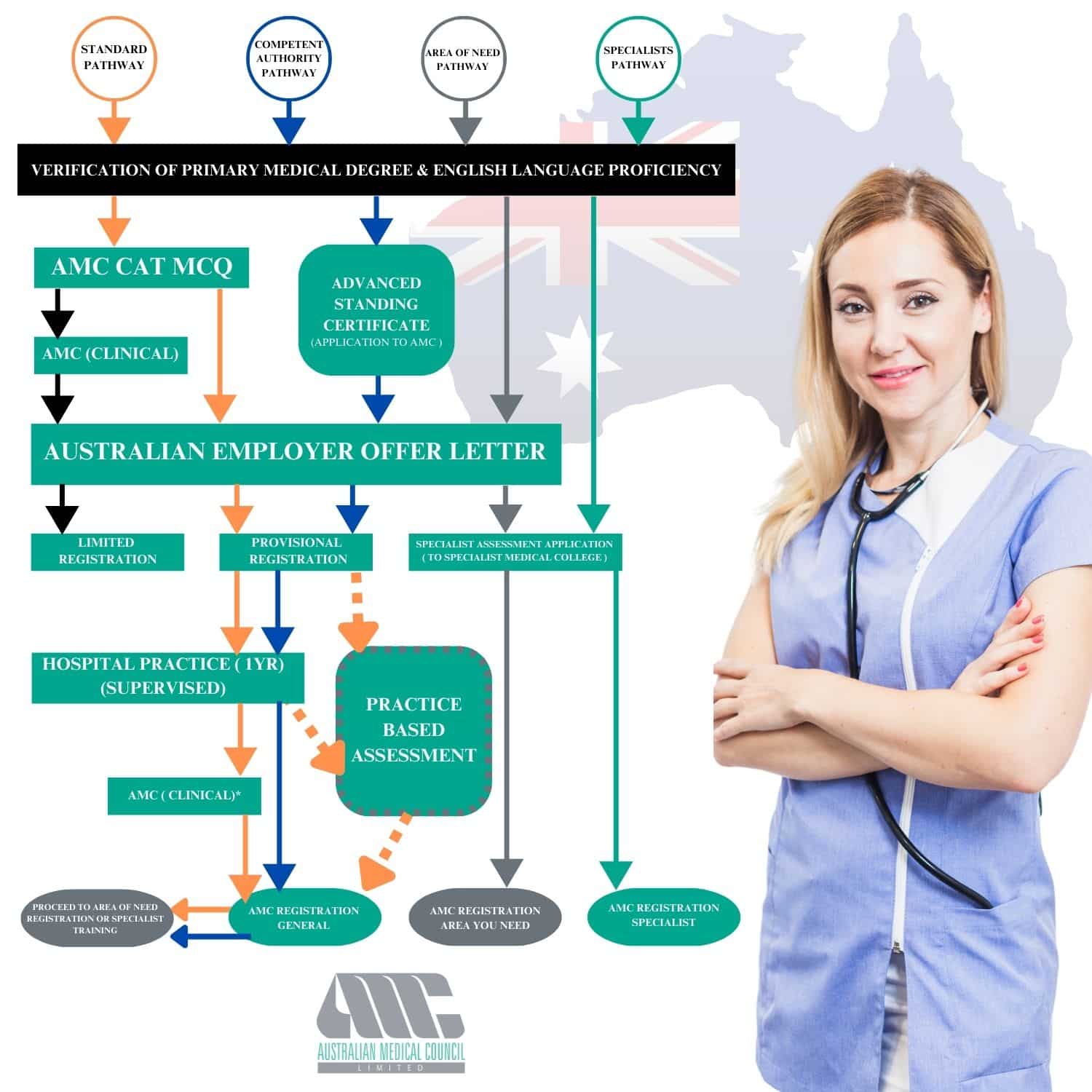
Assessment Pathways to Australian Medical Practice Registration
| Assessment Pathways | Description |
|---|---|
| Australian Medical Council (AMC) Examination | A national examination that assesses the knowledge and clinical skills of international medical graduates (IMGs) seeking registration to practice medicine in Australia. The AMC examination consists of two parts: Part 1 tests the candidate’s basic medical knowledge, while Part 2 assesses their clinical skills. |
| Competent Authority Pathway | A pathway for IMGs who have completed their medical education in countries that have a competent authority agreement with Australia. This pathway requires the applicant to provide evidence of their qualifications and experience, and undergo an assessment of their skills and knowledge by the relevant competent authority. |
| Standard Pathway | A pathway for IMGs who have completed their medical education in a country that does not have a competent authority agreement with Australia. This pathway requires the applicant to provide evidence of their qualifications and experience, and undergo an assessment of their skills and knowledge by an accredited assessing authority. |
| Specialist Pathway | A pathway for specialist medical practitioners who have completed their training overseas and wish to practice in Australia. This pathway requires the applicant to provide evidence of their specialist qualifications and experience, and undergo an assessment of their skills and knowledge by the relevant specialist medical college in Australia. |
| Specialist Pathway – Area of Need | A pathway for specialist medical practitioners who have been identified as having skills and experience in an area of medicine where there is a shortage of specialists in Australia. This pathway requires the applicant to provide evidence of their specialist qualifications and experience, and undergo an assessment of their skills and knowledge by the relevant specialist medical college in Australia. |
| Short-term Training in a Medical Specialty (STP) | A pathway for IMGs who have completed their medical education and are seeking short-term training in a medical specialty in Australia. This pathway requires the applicant to have a job offer from an Australian hospital or health service, and to undergo an assessment of their skills and knowledge by the relevant specialist medical college in Australia. |
Assessment Pathways to Australian Medical Practice Registration
There are two main pathways to medical registration in Australia: the Australian Medical Council (AMC) standard pathway and the competent authority pathway.
Steps for International Medical Graduates to Register as Specialists in Australia
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Check eligibility: International medical graduates must ensure they meet eligibility criteria, including having a recognized medical degree, postgraduate training, and specialist qualifications. |
| 2 | Register with the Australian Medical Council (AMC): International medical graduates must register with the AMC, which assesses their qualifications and suitability for medical practice in Australia. They must provide evidence of their medical qualifications, postgraduate training, and specialist qualifications. |
| 3 | Apply for specialist assessment: International medical graduates can apply for specialist assessment after registering with the AMC. Accredited specialist medical colleges or boards assess the applicant’s specialist qualifications, clinical experience, and professional standing. |
| 4 | Complete necessary training or examinations: Depending on the outcome of the specialist assessment, international medical graduates may need to complete additional training or exams to meet the required standards for practice as a specialist in Australia. The training may take place in Australia or overseas, and exams may be written, clinical, or both. |
| 5 | Obtain registration with the Medical Board of Australia: Once all requirements are met, international medical graduates can apply for registration with the Medical Board of Australia. They need to provide evidence of identity, professional indemnity insurance, and ongoing professional development. |
| 6 | Start practicing as a specialist in Australia: After registration, international medical graduates can start practicing as specialists in Australia, working in hospitals, clinics, or other healthcare settings. They need to meet the same professional and ethical standards as Australian-trained doctors and participate in ongoing professional development. |
Challenges in Australia Medical Council Registration
Best Way To Enter Into Australian Healthcare System
The healthcare system in Australia is highly regarded around the world, and many individuals aspire to pursue a career in medicine in the country. However, entering the Australian healthcare system can be a complex and challenging process, especially for those who are not familiar with the system’s nuances. In this article, we will discuss the ideal way to enter the Australian healthcare system and build a successful career in medicine.
Conventional Agents
One option for those who wish to pursue a career in medicine in Australia is to approach conventional agents. These agents are typically found in many parts of the world and promote medical careers in Australia. However, it is important to note that many of these agents promote a lesser-known non-clinical pathway. This pathway requires a significant investment of money, ranging from 70 lacs to 1 crore, and does not offer individuals the opportunity to practice clinically in Australia. Therefore, if your long-term goal is to practice clinically in Australia, it is advisable to reconsider this option.
Softamo Pathway
The Softamo Pathway is an ideal way for individuals to settle in Australia and practice clinically in the country. To pursue this pathway, individuals need to complete a postgraduate degree in either India or the United States. After completing their postgraduate degree, they can apply to work clinically in Australia through the AMC Australia Specialist Pathway. However, there are two important things individuals need to do before they can pursue this pathway.
Firstly, individuals need to prepare for the AMC CAT MCQ, which is a tough exam. The best way to prepare for this exam is to work with Softamo, an organization that specializes in helping individuals prepare for this exam. Secondly, individuals need to associate with a licensed immigration agent for Australia and apply for immigration to Australia when the time comes. It is important to keep in mind that due to the competition and quota system in Australia, not many seats are available for postgraduate studies in medicine in the country.
Benefits of Softamo Pathway
There are several benefits to pursuing the Softamo Pathway to practice medicine in Australia. Firstly, individuals who pursue this pathway can settle in Australia and build a successful clinical practice in the country. Secondly, Softamo offers comprehensive support to individuals who wish to prepare for the AMC CAT MCQ, ensuring that they are fully equipped to pass the exam. Thirdly, by working with a licensed immigration agent, individuals can navigate the complex immigration process and increase their chances of being granted a visa to work in Australia.
Challenges of Softamo Pathway
While the Softamo Pathway offers several benefits, it is important to be aware of the challenges associated with pursuing this pathway. Firstly, individuals need to invest significant time and money in preparing for the AMC CAT MCQ. Secondly, the competition for postgraduate studies in medicine in Australia is high, and there are limited seats available. Therefore, individuals need to be prepared to work hard and remain persistent in pursuing their goals.

